Kidney infections are majorly caused by viruses or bacteria in your kidneys.
A kidney infection, which is also known as pyelonephritis, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects one or both kidneys. It occurs when bacteria from the bladder or urethra travel up to the kidneys, where they can cause inflammation and damage to the kidney tissue. Kidney infections are more common in women and can occur at any age.
The most common causes of a kidney infection include:
- Bacterial infection: The most common bacteria that cause kidney infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is normally found in the digestive tract.
- Urinary tract blockage: Blockages in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, can cause urine to back up into the kidneys and increase the risk of infection.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or diabetes, are more prone to kidney infections.
- Use of urinary catheters: People who need to use urinary catheters for an extended period are at higher risk of developing a kidney infection.
Symptoms of a kidney infection may include:
- High fever (over 100.4°F)
- Chills
- Back pain or flank pain (on one or both sides)
- Abdominal pain
- Frequent urination
- Painful urination
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Confusion (in older adults)
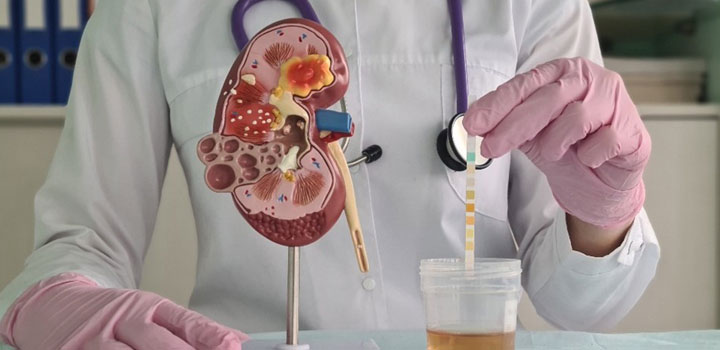
Kidney Infection Diagnosis
After checking your symptoms, your physician will probably perform diagnostic tests including:
- Urine analysis to investigate for blood, pus, and bacteria in your pee.
- Urine culture to check what kind of bacteria you have.
Your doctor may also use these tests:
- Ultrasound or CT scan- The physician may perform this to check for a blockage in your urinary tract, if treatment does not help within 3 days.
- Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG)- To check for problems in your urethra and bladder, it is a type of x-ray.
- Digital rectal exam (for men)- This is a test where a physician inserts a lubricated finger into your anus to check for a swollen prostate.
- Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scintigraphy- This test uses radioactive material to check for kidney infection and damage.
Risk factors:
There are many factors that increase the risk of a kidney infection
- Being female. Bacteria can easily travel from outside the body to the bladder as the urethra is shorter in women than in men, which makes it easier for bacteria to travel from outside the body to the bladder. The infection can spread to the kidneys once in the bladder. Pregnant women are at an increased risk of a kidney infection.
- Blockage in the urinary tract. The risk of a kidney infection is also raised by slowing the flow of urine or anything which makes it harder to fully empty the bladder. This includes a kidney stone, an enlarged prostate gland, or a narrowed urethra.
- Having a weak immune system. The immune system can be weakened by medical conditions which include diabetes and HIV. Certain medicines also can lower immunity which can include drugs taken after an organ transplant that help prevent rejection.
- Having damage to nerves around the bladder. Spinal cord or nerve damage can block the feeling of a bladder infection, which makes it hard to know when an infection travels to the kidneys.
- Using a urinary catheter. To drain urine from the bladder urinary catheters are used. Catheters are sometimes used after a diagnostic test or surgical procedure. They are also used for people who are on bed rest.
- Urine is flowing the wrong way. Small amounts of urine flow from the bladder back into the tubes that connect the bladder and kidneys in vesicoureteral reflux. People who are suffering from this condition are at higher risk of kidney infections when they are kids and when they become adults.
Complications:
Kidney infection if left untreated, can lead to possibly serious complications, such as:
- Kidney scarring. This can lead to high blood pressure, kidney failure, and chronic kidney disease.
- Blood poisoning. A kidney infection can cause bacteria to spread through the bloodstream as kidneys filter waste from the blood and return the filtered blood to the rest of the body.
- Pregnancy complications. A kidney infection that occurs during pregnancy can increase the chances of low birth baby weight.
A kidney infection needs immediate medical treatment. An infection can cause lasting damage to the kidneys, if not treated properly. In such cases, bacteria can spread to the bloodstream and cause a dangerous infection. Treatment of kidney infection typically involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Your doctor may prescribe a 7–14-day course of antibiotics depending on the severity of the infection. Pain relievers may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms such as fever and pain.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for intravenous antibiotics or other treatments. It is important to stay well hydrated and get plenty of rest while recovering from a kidney infection.
To prevent kidney infections, it is important to maintain good hygiene habits, such as wiping front to back after using the bathroom and urinating after sexual activity. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding irritants such as harsh soaps or bubble baths can also help reduce the risk of kidney infections.
To schedule an appointment with us, please visit – https://clinicalrenal.com/all-locations/. We are dedicated kidney specialists serving Southeast Pennsylvania for over 40 years.